Gravitational Acceleration on the Planets of the Solar System and Their Satellites
This table contains the values of
the acceleration of gravity on the surface of the planets of the solar system and their satellites.
Free fall acceleration is the acceleration that a body acquires under the action of a gravitational force near the surface of celestial bodies in outer space.
The SI unit of gravitational acceleration is meters per second squared.
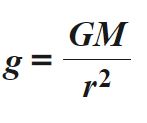 According to the law of universal gravitation, the acceleration on the surface of a astronomical object (stars, planets, etc.)
is equal to the ratio of the product of the gravitational constant G and the mass of the object by the square of the radius of the object.
According to the law of universal gravitation, the acceleration on the surface of a astronomical object (stars, planets, etc.)
is equal to the ratio of the product of the gravitational constant G and the mass of the object by the square of the radius of the object.
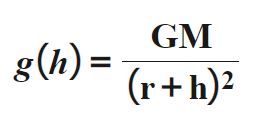 The gravitational acceleration at a height h above the surface of a space object is calculated using this formula.
The gravitational acceleration at a height h above the surface of a space object is calculated using this formula.
G = 6.67 × 10-11 N × m2 / kg2
Free fall acceleration g on the Earth's surface is 9.780327 m/s2
| The Sun | 273.1 m/s2 |
| Mercury | 3.7 m/s2 |
| Venus | 8.87 m/s2 |
| Earth | 9.780327 m/s2 |
| Moon | 1.62 m/s2 |
| Mars | 3.711 m/s2 |
| Phobos | 0.0019 m/s2 |
| Deimos | 0.0039 m/s2 |
| Ceres | 0.27 m/s2 |
| Jupiter | 23.95 m/s2 |
| Io | 1.796 m/s2 |
| Europa | 1.315 m/s2 |
| Ganymede | 1.428 m/s2 |
| Callisto | 1.235 m/s2 |
| Saturn | 10.44 m/s2 |
| Titan | 1.352 m/s2 |
| Enceladus | 0.111 m/s2 |
| Tethys | 0.145 m/s2 |
| Rhea | 0.264 m/s2 |
| Dione | 0.231 m/s2 |
| Iapetus | 0.223 m/s2 |
| Mimas | 0.064 m/s2 |
| Uranus | 8.86 m/s2 |
| Pack | 0.028 m/s2 |
| Miranda | 0.079 m/s2 |
| Ariel | 0.27 m/s2 |
| Umbriel | 0.23 m/s2 |
| Titania | 0.379 m/s2 |
| Oberon | 0.346 m/s2 |
| Neptune | 11.09 m/s2 |
| Triton | 0.779 m/s2 |
| Nereid | 0.0715 m/s2 |
| Proteus | 0.07 m/s2 |
| Pluto | 0.617 m/s2 |
| Charon | 0.278 m/s2 |
| Haumea | 0.44 m/s2 |
| Makemake | 0.4 m/s2 |
| Eris | 0.82 m/s2 |
See also